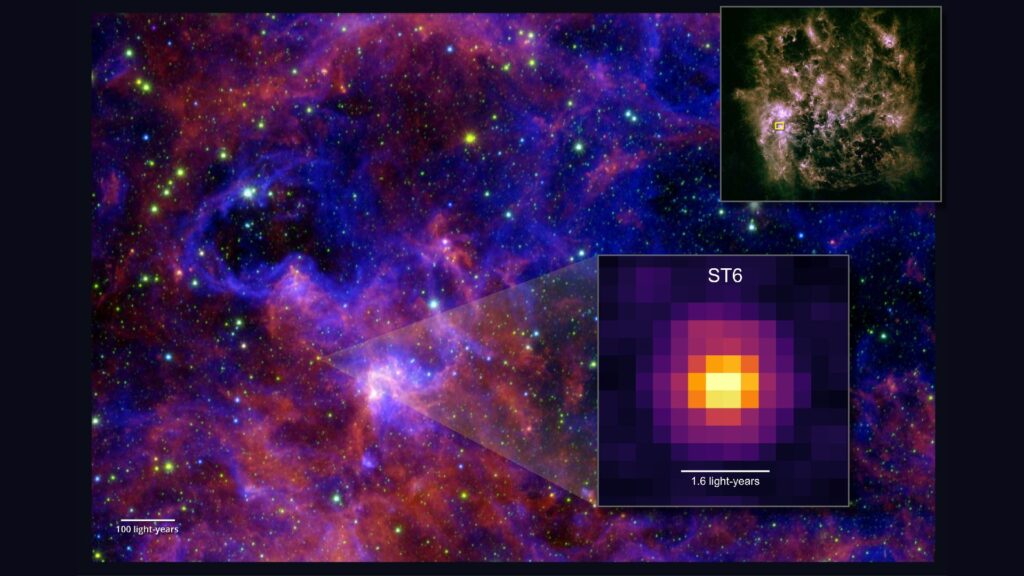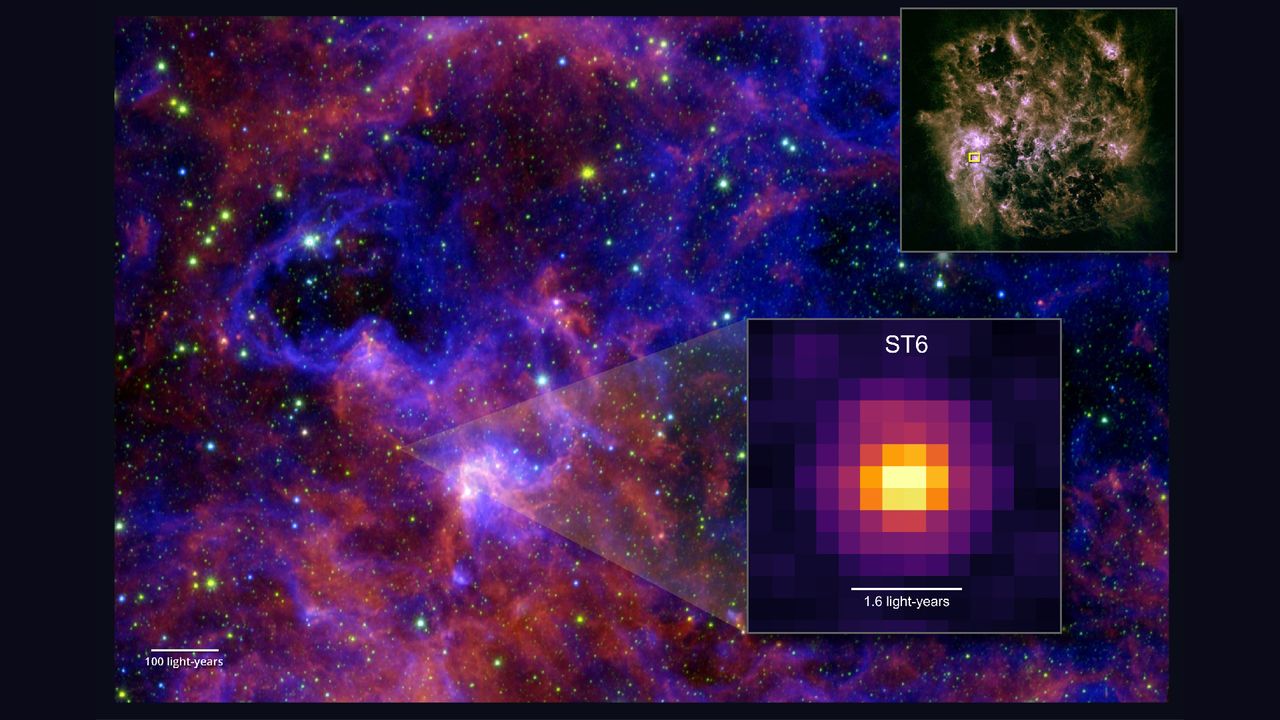
For the first time, scientists have spotted multiple complex building blocks of life in the ice around a star outside the Milky Way.
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), researchers detected five large, carbon-based compounds around a protostar in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small galaxy that orbits closely to the Milky Way. The findings could help scientists learn how complex molecules formed in the early universe, according to a study published Oct. 20 in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
“What we learn in the Large Magellanic Cloud, we can apply to understanding these more distant galaxies from when the universe was much younger,” study co-author Marta Sewilo, an astronomer at the University of Maryland and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, said in a statement. “The harsh conditions tell us more about how complex organic chemistry can occur in these primitive environments where much fewer heavy elements like carbon, nitrogen and oxygen are available for chemical reactions.”
In March 2024, the researchers pointed the JWST at a developing star, dubbed ST6, in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Using instruments that measure infrared light, they discovered five complex carbon-based molecules in the ice around the star: methanol, acetaldehyde, ethanol, methyl formate and acetic acid.
Of the five molecules, only methanol has been previously detected in protostars outside the Milky Way. Acetic acid, the main component in vinegar, had never even been conclusively found in space ice before.
“Before Webb, methanol had been the only complex organic molecule conclusively detected in ice around protostars, even in our own galaxy,” Sewilo said. “The exceptional quality of our new observations helped us gather an immense amount of information from a single spectrum, more than we’ve ever had before.”
The researchers also found signals that might be caused by a chemical called glycolaldehyde, although further study will be needed to confirm its presence. Glycolaldehyde can react with other molecules to form a type of sugar called ribose, an important component of ribonucleic acid (RNA), which is essential for life.
Finding such complex molecules in the Large Magellanic Cloud suggests that chemical reactions on the surfaces of dust grains can produce complex molecules even under harsh conditions, the researchers said. In future studies, the team plans to look for these and similar molecules around other protostars, both in the Milky Way and in nearby galaxies.
“With this discovery, we’ve made significant advancements in understanding how complex chemistry emerges in the universe and opening new possibilities for research into how life came to be,” Sewilo said in the statement.